Research Interest
Head: Dr. habil. Helmut Bäumlein
We focus on the molecular dissection of genetic and epigenetic pathways that control sexual and asexual plant reproductive development. To answer our research questions we use genetic, molecular and imaging techniques in the model plant Arabidopsis (dicot), the parthenogenetic ´Salmon´wheat lines as well as the two apomictic species Hypericum and Boechera.
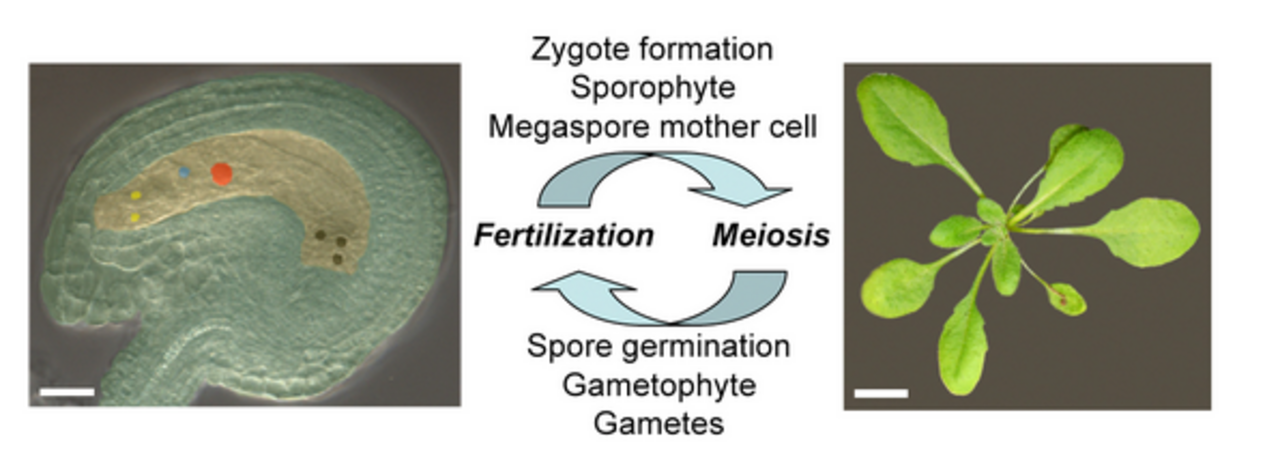
Plant development is a recurrent process occurring in two distinct alternating generations, gametes-producing gametophyte and the spore-producing sporophyte. Plant gametes are contained in plant-specific haploid organisms known as the female (embryo sac) and male (pollen) gametophytes that are independently derived via meiotic reduction of the corresponding diploid spores. Fertilisation of haploid gametes (egg and sperm cells) leads to the development of the diploid embryo sporophyte. In flowering plants, a second fertilization event occurs in which the second female gamete, known as the homo-diploid central cell, is fertilized by an additional haploid sperm cell, leading to the development of triploid endosperm that nourishes the embryo. After early embryogenesis, the seed matures via synthesis of storage compounds as well as acquisition of desiccation tolerance and dormancy. Subsequently, the mature seed germinates into the whole plant sporophyte.
While most plants reproduce sexually, some plant species in the wild reproduce asexually by a process known as apomixis. Both meiosis and egg fertilization are either avoided or circumvented during apomictic events such as apomeiosis and parthenogenesis, respectively; thereby, the offspring are the clonal replica of the mother plant.
Molecular dissection of these coordinated developmental events of both sexual and asexual plant reproduction is an exciting basic research field in plant biology and provides important information required for biotechnological applications such as food technology (e.g. cereal endosperm) and transfer of elite crop traits like heterosis via apomixis.